Bachelor of Chemical Process Engineering with Honours
This academic program is accredidated by the Board of Engnieers Malaysia 2017-2028, which the programme complies with engineering contents as in the Engineering Accreditation Council (EAC) and the Washington Accord.
A balanced curriculum is designed such that students would have the knowledge and competency to work professionally as an engineer. The curriculum covers basic engineering emphasis and specialization in chemical engineering. The humanities elements are also embedded in to produce well-rounded engineers who are morally sound and ethical, and able to communicate effectively. Chemical Process Engineering program was designed for students who wish to acquire a solid foundation in chemical engineering with deep knowledge of the principles and practice of chemical engineering.
Chemical Process Engineering (SMJC) courses are organized into 8 semesters. Semester 1 covers basic knowledge such as communication in English, Programming, Engineering Mathematics, and Introduction to Chemical Process Engineering. During the second semester, students will be introduced to basic chemical engineering through Thermodynamics. In addition students will also be introduced to general university courses such as Graduate Success Attributes. The following year (Semester 3 and 4) will cover several chemistry and basic chemical engineering courses to develop strong fundamentals, such as Mass and Energy Balance, Fluid mechanics, Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, and Transport Phenomena. In the 5th until 8th semester, students are introduced to further chemical engineering principles, undergraduate research project, and undergo industrial training for minimum of 12 weeks. Graduates of this program will also be prepared for entry into post graduate education.
- Programme Educational Objectives (PEOs)
- Programme Outcome (PO)
- Program Structure
- Knowledge Profile
- Entry Requirement
- Career Opportunity
| PEO | PEO Statements | Indicators (3 – 5 years) |
| PEO1 | Generate innovative ideas or products in local or international industry or government and to work in multidisciplinary teams in implementing these solutions in practice. |
>75% of graduates work scope related to analysis, planning and project management. >40% of graduates lead a unit. >30% of graduates work related to Chemical Process Engineering disciplines. |
| PEO2 | Establish themselves in a diverse range of careers in technology driven transdisciplinary field with Japanese work culture or engage in business opportunities. |
>30% of graduates work in Japanese companies or Japanese related firms. >30% of graduates are involved in business dealing with Japanese companies. |
| PEO3 |
Demonstrate ethical responsibility through involvement with community and/or professional organizations and/or contribute towards a sustainable society. |
>10% of graduates involved in NGOs. >10% of graduates attained professional memberships in Professional Bodies. |
| PEO4 | Recognise the importance of and engage in life-long learning through formal graduate level education. |
>30% of graduates attended courses to broaden their knowledge. >10% of graduates pursuing further studies. >15% of graduates involved in research works. |
| A: Technical Knowledge and Competencies | |
| PLO 1 |
Engineering Knowledge Ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, engineering and humanities fundamentals and system Chemical Process Engineering’s to the solution of complex engineering problems. |
| PLO 2 |
Problem Analysis Ability to identify, formulate, analyse and research literature on complex engineering problems to reach substantiated conclusions using first principles of mathematics, natural sciences and engineering sciences. |
| PLO 3 |
Design/Development Ability to design and develop system Chemical Process Engineering’s solution to complex engineering problems that meet specified needs with appropriate consideration for public health and safety, cultural, societal, and environmental considerations. |
| B: Generic skills | |
| PLO 4 |
Investigation Ability to conduct investigation into complex problems on Chemical Process Engineering’s systems using research based knowledge and research methods learned in iKohza and synthesis of information to provide valid conclusions. |
| PLO 5 |
Modern Tool Usage Ability to apply appropriate techniques, resources, and modern engineering and IT tools, including prediction and modelling to complex engineering activities with an understanding of the limitations. |
| PLO 6 |
The Engineer and Society Ability to apply contextual knowledge to assess societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues and his/her responsibilities relevant to professional engineering practice |
| PLO 7 |
Environment and Sustainability Ability to explain, compare and summarize the impact of professional engineering solutions in societal and environmental contexts and demonstrate knowledge of and need for sustainable development. |
| PLO 8 |
Ethics Ability to apply ethical principles and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities and norms of engineering practice, in multicultural society based on Islamic, ASEAN and Japanese culture |
| PLO 9 |
Communication Ability to communicate effectively on complex engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large, sometimes in Japanese |
| PLO 10 |
Individual and Team Work Ability to function effectively as an individual, and as a member or leader in diverse teams and in multi-disciplinary settings. |
| PLO 11 |
Life-long Learning Ability to recognize the need for, and have the preparation and ability to engage in independent and life-long learning in the broadest context of technological change. |
| PLO 12 |
Engineering Project Management and Finance Ability to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of engineering and management principles and apply these to one’s own work. |
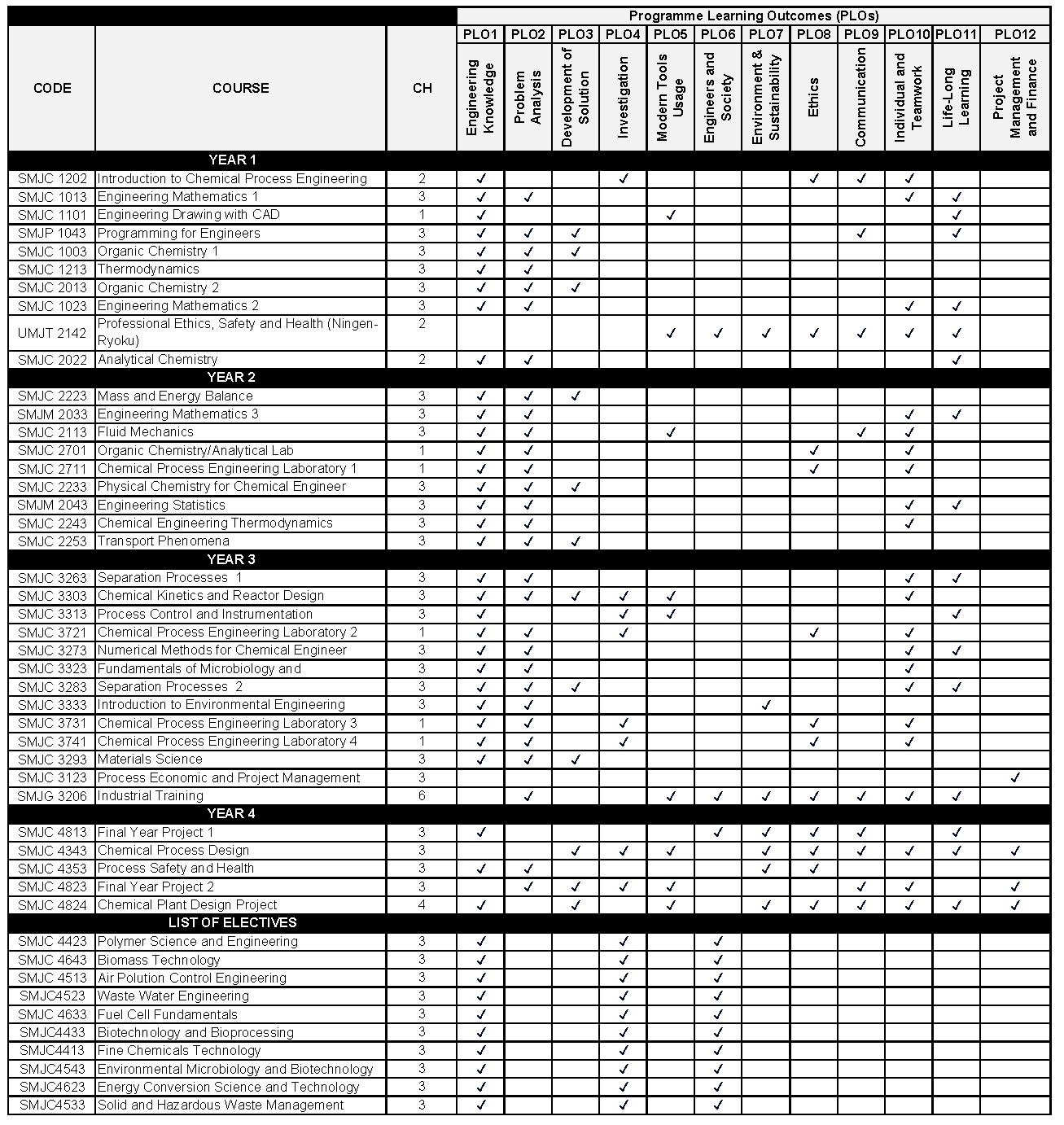
Mapping of PLO toward Subject
For 2022/2023 intake onwards:
| YEAR 1 SEMESTER 1 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 1202 | Introduction to Chemical Process Engineering | 2 |
| SMJM 1013 | Engineering Mathematics 1 | 3 |
| SMJC 1101 | Engineering Drawing with CAD | 1 |
| SMJP 1043 | Programming for Engineers | 3 |
| SMJC 1003 | Organic Chemistry 1 | 3 |
| UHMS 1182 | Appreciation of Ethics and Civilisation | 2 |
| UHLM 1012 | Malay Language for Communication 2 | |
| UHLB 1112 | English Communication Skills | HW |
| Total Credits | 14 | |
| YEAR 1 SEMESTER 2 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 1213 | Thermodynamics | 3 |
| SMJM 1023 | Engineering Mathematics 2 | 3 |
| UHLJ 1112 | Japanese for Communication 1 | 2 |
| SMJC 2013 | Organic Chemistry 2 | 3 |
| UMJT 2142 | Professional Ethics, Safety and Health(Ningen-Ryoku) | 2 |
| ULRS 1012 (ULRS 1032) |
Value and Identify (Integrity and Anti-Bribery) – for 2023/2024 intake onwards |
2 |
| SMJC 2022 | Analytical Chemistry | 2 |
| Total Credits | 17 | |
| YEAR 2 SEMESTER 1 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 2223 | Mass and Energy Balance | 3 |
| SMJC 2113 | Fluid Mechanics | 3 |
| SMJM 2033 | Engineering Mathematics 3 | 3 |
| SHLJ 2252 | Japanese for Communication 2 | 2 |
| UHLB 2122 | Professional Communication Skills 1 | 2 |
| UHIS 1022 | Philosophy and Current Issue | 2 |
| U*** ***3 | Free Elective | 3 |
| Total Credits | 18 | |
| YEAR 2 SEMESTER 2 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 2701 | Organic Chemistry/Analytical Lab | 1 |
| SMJC 2711 | Chemical Process Engineering Laboratory 1 | 1 |
| SMJC 2233 | Physical Chemistry for Chemical Engineer | 3 |
| SMJC 2243 | Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics | 3 |
| SMJC 2253 | Transport Phenomena | 3 |
| SMJM 2043 | Engineering Statistics | 3 |
| SHLJ 2352 | Japanese for Communication 3 | 2 |
| UKQF 2**2 | Co-Curriculum/Service Learning | 2 |
| Total Credits | 18 | |
| YEAR 3 SEMESTER 1 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 3263 | Separation Process 1 | 3 |
| SMJC 3303 | Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design | 3 |
| SMJC 3313 | Process Control and Instrumentation | 3 |
| SMJC 3273 | Numerical Methods for Chemical Engineers | 3 |
| SMJC 3323 | Fundamentals of Microbiology and Biotechnology | 3 |
| SMJC 3721 | Chemical Process Engineering Laboratory 2 | 1 |
| ULRS3032 | Entrepreneurship & Innovation | 2 |
| Total Credits | 18 | |
| YEAR 3 SEMESTER 2 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 3283 | Separation Process 2 | 3 |
| SMJC 3333 | Introduction to Environmental Engineering | 3 |
| SMJC 3293 | Materials Science | 3 |
| SMJC 4353 | Process Safety and Health | 3 |
| SMJC 3731 | Chemical Process Engineering Laboratory 3 | 1 |
| SMJC 3741 | Chemical Process Engineering Laboratory 4 | 1 |
| UHLB 3132 | Professional Communication Skills 2 | 2 |
| Total Credits | 16 | |
| YEAR 3 SEMESTER 3 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJG 3206 | Industrial Training | 6 |
| YEAR 4 SEMESTER 1 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 4813 | Final Year Project 1 | 3 |
| SMJC 4343 | Chemical Process Design | 3 |
| SMJC 3123 | Process Economic and Project Management | 3 |
| SMJC 4**3 | Elective 1 | 3 |
| SMJC 4**3 | Elective 2 | 3 |
| Total Credits | 15 | |
| YEAR 4 SEMESTER 2 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 4823 | Final Year Project 2 | 3 |
| SMJC 4824 | Chemical Plant Design Project | 4 |
| SMJC 4**3 | Elective 3 | 3 |
| SMJC 4**3 | Elective 4 | 3 |
| Total Credits | 13 | |
| GRAND TOTAL CREDITS | 135 | |
For 2019/2020 – 2021/2022 intake:
| YEAR 1 SEMESTER 1 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 1202 | Introduction to Chemical Process Engineering | 2 |
| SMJM 1013 | Engineering Mathematics 1 | 3 |
| SMJC 1101 | Engineering Drawing with CAD | 1 |
| SMJP 1043 | Programming for Engineers | 3 |
| UHLB 1112 | English Communication Skills | 2 |
| UBSS 1032 | Introduction to Entrepreneurship | 2 |
| UHIS 1022 | Philosophy and Current Issue (*for local & international students) | 2 |
| Total Credits | 15 | |
| YEAR 1 SEMESTER 2 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 1003 | Organic Chemistry 1 | 3 |
| SMJC 1213 | Thermodynamics | 3 |
| SMJM 1023 | Engineering Mathematics 2 | 3 |
| SHLJ 1152 | Japanese for Communication 1 | 2 |
| UHLB 2122 | Advanced Academic English Skills | 2 |
| UMJT 2142 | Professional Ethics, Safety and Health(Ningen-Ryoku) | 2 |
| UHMT 1012 | Graduate Success Attributes | 2 |
| Total Credits | 17 | |
| YEAR 2 SEMESTER 1 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 2013 | Organic Chemistry 2 | 3 |
| SMJC 2223 | Mass and Energy Balance | 3 |
| SMJM 2033 | Engineering Mathematics 3 | 3 |
| SHLJ 2252 | Japanese for Communication 2 | 2 |
| SMJC 2022 | Analytical Chemistry | 2 |
| SMJC 2113 | Fluid Mechanics | 3 |
| UHMS 1182 | Appreciation of Ethics and Civilisation (*For local students) | 2 |
| UHLM 1012 | Malay Language for Communication 2 (*For international students) | |
| Total Credits | 18 | |
| YEAR 2 SEMESTER 2 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 2701 | Organic Chemistry/Analytical Lab | 1 |
| SMJC 2711 | Chemical Process Engineering Laboratory 1 | 1 |
| SMJC 2233 | Physical Chemistry for Chemical Engineer | 3 |
| SMJC 2243 | Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics | 3 |
| SMJC 2253 | Transport Phenomena | 3 |
| SMJM 2043 | Engineering Statistics | 3 |
| SHLJ 2352 | Japanese for Communication 3 | 2 |
| UHIT 2302 | The Thought of Science and Technology | 2 |
| Total Credits | 18 | |
| YEAR 3 SEMESTER 1 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 3263 | Separation Process 1 | 3 |
| SMJC 3303 | Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design | 3 |
| SMJC 3313 | Process Control and Instrumentation | 3 |
| SMJC 3721 | Chemical Process Engineering Laboratory 2 | 1 |
| SMJC 3273 | Numerical Methods for Chemical Engineer | 3 |
| SMJC 3323 | Fundamentals of Microbiology and Biotechnology | 3 |
| Total Credits | 16 | |
| YEAR 3 SEMESTER 2 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 3283 | Separation Process 2 | 3 |
| SMJC 3333 | Introduction to Environmental Engineering | 3 |
| SMJC 3731 | Chemical Process Engineering Laboratory 3 | 1 |
| SMJC 3741 | Chemical Process Engineering Laboratory 4 | 1 |
| SMJC 3293 | Materials Science | 3 |
| UKQT 3001 | Excel (Extra-Curricular Experientual Learning) | 1 |
| SMJC 3123 | Process Economic and Project Management | 3 |
| UHLB 3162 | English for Professional Purposes | 2 |
| Total Credits | 17 | |
| YEAR 3 SEMESTER 3 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJG 3206 | Industrial Training | 6 |
| YEAR 4 SEMESTER 1 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 4813 | Final Year Project 1 | 3 |
| SMJC 4343 | Chemical Process Design | 3 |
| SMJC 4353 | Process Safety and Health | 3 |
| SMJC 4**3 | Elective 1 | 3 |
| SMJC 4**3 | Elective 2 | 3 |
| Total Credits | 15 | |
| YEAR 4 SEMESTER 2 | ||
| CODE | COURSE | CREDITS |
| SMJC 4823 | Final Year Project 2 | 3 |
| SMJC 4824 | Chemical Plant Design Project | 4 |
| UKQF 2**2 | Co-Curiculum/Service Learning | 2 |
| SMJC 4**3 | Elective 3 | 3 |
| SMJC 4**3 | Elective 4 | 3 |
| Total Credits | 15 | |
| SUBTOTAL | 137 | |
Elective subjects:
| Electives (take any four subjects, subject to availability) | ||
| Group 1: Sustainable Resources | ||
| SMJC 4413 | Fine Chemicals Technology | 3 |
| SMJC 4423 | Polymer Science and Engineering | 3 |
| SMJC 4433 | Biotechnology and Bio-Processing | 3 |
| SMJC 4443 | Fundamentals and Application of Bio-Sensors | 3 |
| Group 2: Sustainable Environment | ||
| SMJC 4513 | Air Pollution Control Engineering | 3 |
| SMJC 4523 | Waste Water Engineering | 3 |
| SMJC 4533 | Solid and Hazardous Waste Management | 3 |
| SMJC 4543 | Environmental Microbiology and Biotechnology | 3 |
| Group 3: Sustainable Energy | ||
| SMJC 4613 | Power Plant Engineering | 3 |
| SMJC 4623 | Energy Conversion Science and Technology | 3 |
| SMJC 4633 | Fuel Cell Fundamentals | 3 |
| SMJC 4643 | Biomass Technology | 3 |
In our SMJC programme, elements of complex problem solving and complex engineering activities are embedded through selected core chemical engineering subjects. The curriculum is also designed to encompass all knowledge profiles as stipulated in the Engineering Programme Accreditation Standard.
The definition of complex problem solving, complex engineering activities and knowledge profile is listed as follows:
a) Definition of Complex Problem Solving
| No. | Attribute | Complex problems have characteristic WP1 and some or all of WP2 to WP7: |
| WP1 | Depth of Knowledge Required |
Cannot be resolved without in-depth engineering knowledge at the level of one or more of WK3, WK4, WK5, WK6 or WK8 which allows a fundamental-based, first principles analytical approach. |
| WP2 | Range of conflicting requirements |
Involve wide-ranging or conflicting technical, engineering and other issues |
| WP3 | Depth of analysis required | Have no obvious solution and require abstract thinking, originality in analysis to formulate suitable models. |
| WP4 | Familiarity of issues | Involve infrequently encountered issues. |
| WP5 | Extent of applicable codes | Are outside problems encompassed by standards and codes of practice for professional engineering. |
| WP6 | Extent of stakeholder involvement and level of conflicting requirements |
Involve diverse groups of stakeholders with widely varying needs. |
| WP7 | Interdependence | Are high level problems including many component parts or subproblems. |
b) Definition of Complex Engineering Activities
| No. | Attribute | Complex activities mean (engineering) activities or projects that have some or all of the following characteristics: |
| EA1 | Range of resources | Involve the use of diverse resources (and for this purpose resources includes people, money, equipment, materials, information and technologies). |
| EA2 | Level of interactions | Require resolution of significant problems arising from interactions between wide ranging or conflicting technical, engineering or other issues. |
| EA3 | Innovation | Involve creative use of engineering principles and research-based knowledge in novel |
| EA4 | Consequences to society and the environment |
Have significant consequences in a range of contexts, characterised by difficulty of prediction and mitigation. |
| EA5 | Familiarity | Can extend beyond previous experiences by applying principlesbased approaches. |
c) Knowledge Profile
| No. | Knowledge Profile |
| WK1 | A systematic, theory-based understanding of the natural sciences applicable to the discipline. |
| WK2 | Conceptually-based mathematics, numerical analysis, statistics and formal aspects of computer and information science to support analysis and modelling applicable to the discipline. |
| WK3 | A systematic, theory-based formulation of engineering fundamentals required in the engineering discipline. |
| WK4 | Engineering specialist knowledge that provides theoretical frameworks and bodies of knowledge for the accepted practice areas in the engineering discipline; much is at the forefront of the discipline. |
| WK5 | Knowledge that supports engineering design in a practice area. |
| WK6 | Knowledge of engineering practice (technology) in the practice areas in the engineering discipline. |
| WK7 | Comprehension of the role of engineering in society and identified issues in engineering practice in the discipline: ethics and the professional responsibility of an engineer to public safety; the impacts of engineering activity: economic, social, cultural, environmental and sustainability. |
| WK8 | Engagement with selected knowledge in the research literature of the discipline. |
The entry to the program could be going through
- UPU (Ministry of Higher Education) – Local Candidate – October Intake
- UTM International Degree Program (UTM Space) – Local/International Candidate – October and March Intake
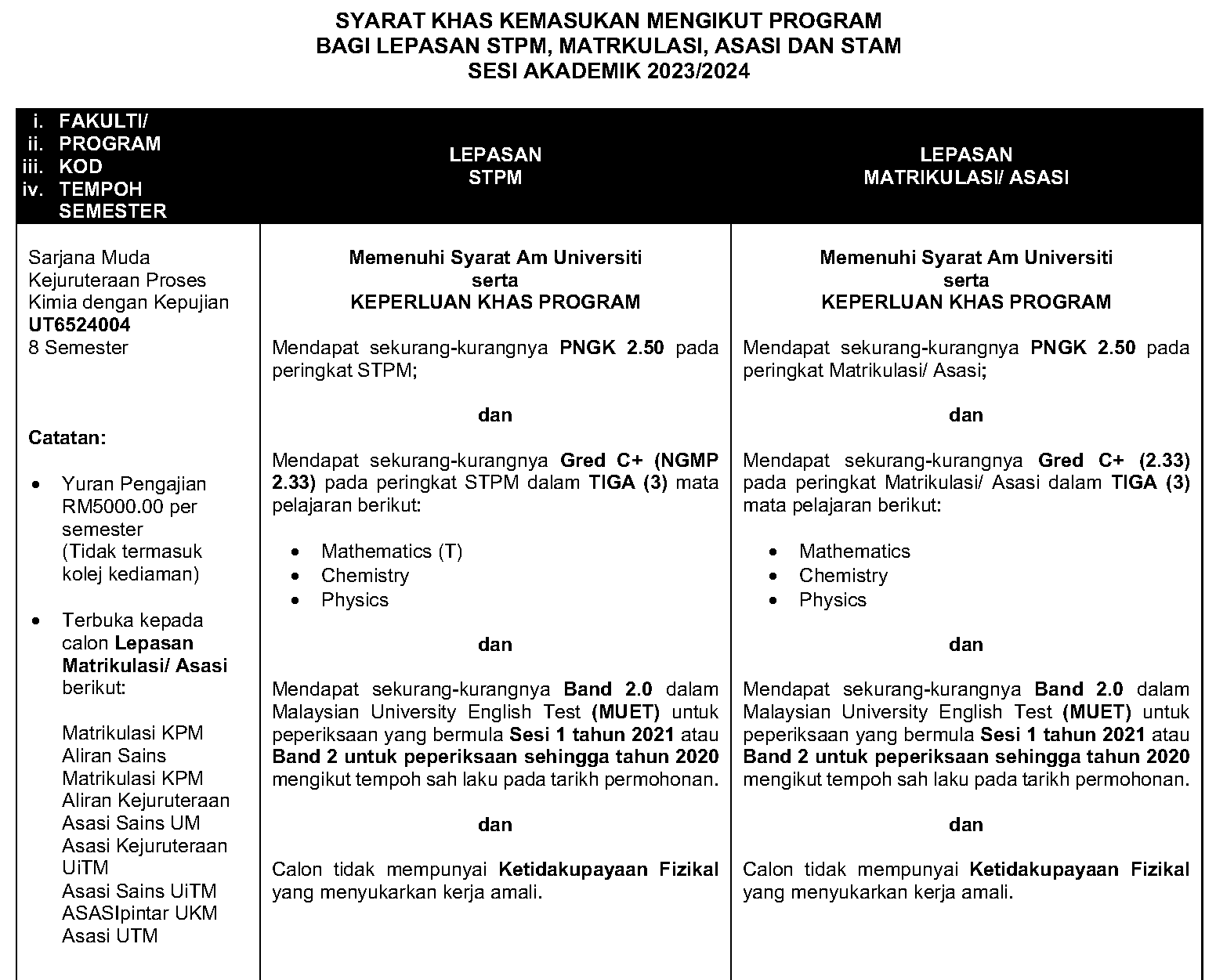
The Entry Requirement – UPU (2023/2024 Intake)
Syarat Am Universiti – LINK
| LEPASAN STPM |
Lulus Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia (SPM)/setaraf dengan mendapat Kepujian dalam Bahasa Melayu/Bahasa Malaysia atau kepujian Bahasa Melayu/ Bahasa Malaysia Kertas Julai; dan Lulus Peperiksaan Sijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia (STPM) dengan sekurang-kurangnya:
Mendapat sekurang – kurangnya Tahap 1 (Band 1) dalam Malaysian University English Test (MUET). |
| LEPASAN STAM |
|
| LEPASAN MATRIKULASI/ ASASI |
|
| LEPASAN DIPLOMA |
|
| LEPASAN KELAYAKAN SETARAF (A-LEVEL/IB/ AUSMAT) |
|
| LEPASAN DIPLOMA VOKASIONAL MALAYSIA (DVM) |
|
Syarat Khas
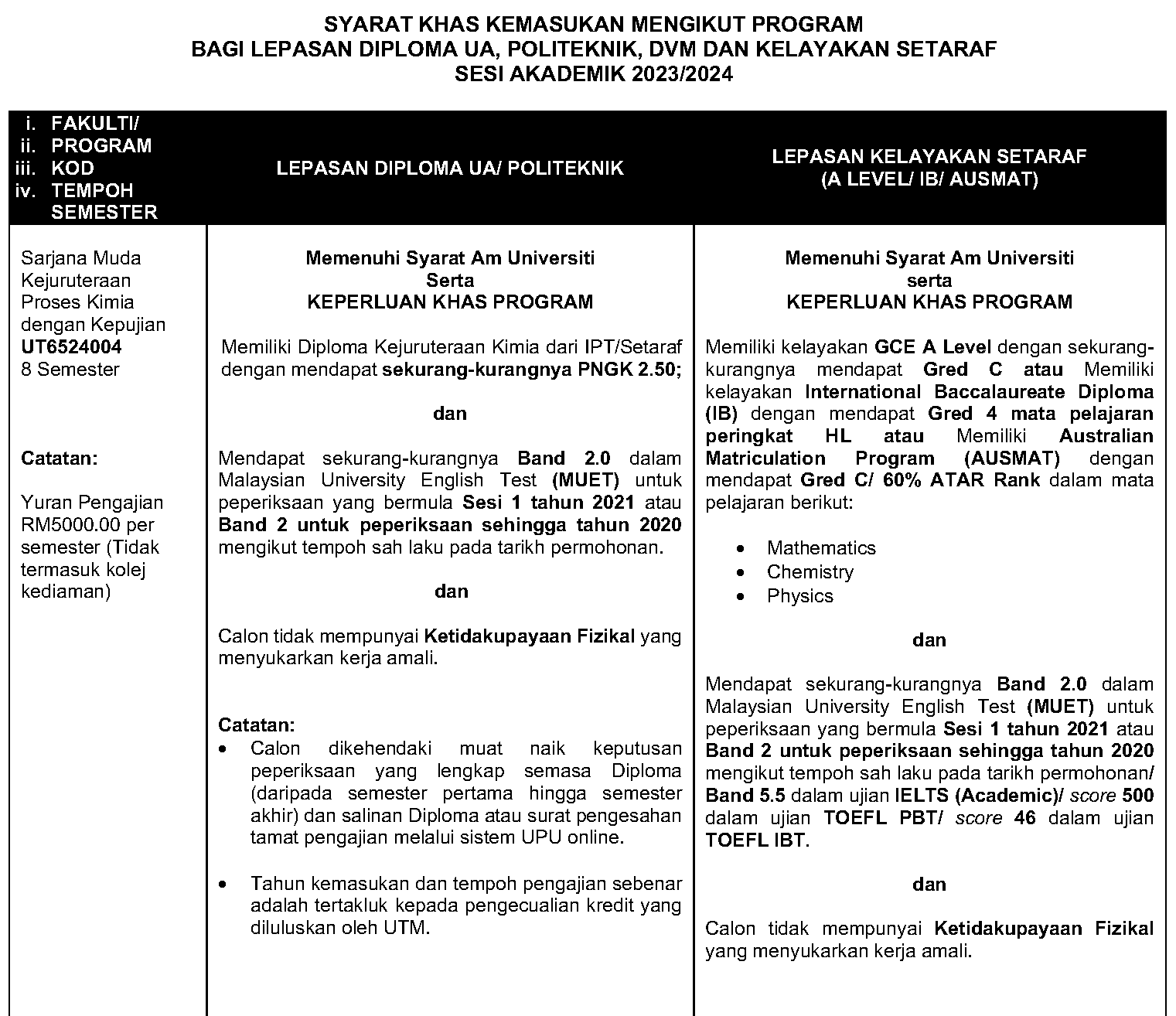
The Entry Requirement – UTM International Degree (2023/2024 Intake)
General Requirement – LOCAL – LINK
- Pass Sijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia (STPM) or equivalent with a minimum of Grade C (NGMP 2.00) in General Studies; and Grade C (NGMP 2.00) in TWO (2) other Subjects; OR
- Pass Sijil Tinggi Agama Malaysia (STAM) with a minimum grade of Jayyid Jiddan; OR
- Pass KPM Matriculation/Foundation recognized by the Malaysian Government and approved by the University Senate with a minimum CGPA of 2.00; OR
- Pass Diploma or any other equivalent qualification recognized by the Malaysian Government and approved by the University Senate; OR
- Pass A Level/ International Baccalaureate / Australian Matriculation (AUSMAT);
AND
- Pass Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia (SPM) with at least Credit in Bahasa Melayu/Bahasa Malaysia or Credit in Bahasa Melayu/ Bahasa Malaysia July Paper,
- Obtained at least Band 2 in the Malaysian University English Test (MUET),
- Meet the faculty specific requirements.
General Requirement – INTERNATIONAL – LINK
- A Senior High School / Senior Secondary School / Other Equivalent Pre-University Examinations from the Government School (12 Years). OR
- A-Level / Diploma in the related field; OR
- Other certificates recognized by the Malaysia Qualifications Agency (MQA) & senate of the university
AND
- Meet the entry requirement based on country
- Pass the English Proficiency Requirements
|
English Language Test |
Required Bands and Score |
| Malaysian University English Test (MUET) | Band 4.0 and above |
| International English Language Testing System (IELTS) | Band 5.5 and above |
| Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) iBT | Score of 46 and above |
| The Pearson Test of English (PTE Academic / PTE Academic Online) | Score of 51 and above |
| Cambridge English Qualification (CEQ) – B2 First (FCE), C1 Advanced (CAE), C2 Proficiency (CPE) | Score of 160 and above |
| Certified Intensive English Programme (CIEP – ELS) | Complete level 108 and above |
IMPORTANT NOTE:
1. Students who do not meet the English language proficiency standards or requirements are required to attend:
- Intensive English Programme (IEP) conducted by the UTM Language Academy and obtain a minimum score in MUET / IELTS / TOEFL / Pearson Test of English / Cambridge English Qualification, OR
- Certified Intensive English Programme (CIEP) conducted by the ELS Language Centre and completed Level 108.
OTHER EXEMPTION FOR UNDERGRADUATE INTERNATIONAL STUDENT:
1. Candidates from International Schools, A-level and International Baccalaureate qualifications are exempted from the UTM English language requirement and Bridging Programme.
2. Candidates from the UTM Foundation or other Foundation programmes in Malaysia are exempted from the UTM English language requirement and Bridging Programme.
For more details on English Language Requirements, kindly visit this link: https://admission.utm.my/english-language-requirements-3/
Graduates from this program can seek employment opportunities as process engineers, design engineers, chemical engineers, research engineers, technical sales engineers, commissioning engineers, service engineers in the chemical and biochemical industry, the oil and gas industry, the water and waste water treatment industry, the power station, the food industry, the pharmaceutical industry, the electronic industry, the heavy industry etc. Graduates of this program will also be prepared for entry into post graduate education either in MJIIT or other universities worldwide.